
I am Munish, a PhD candidate working at the Institute of Genetics and Development Rennes. I have completed my BS-MS degree at the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Mohali. During my master’s thesis project, I worked under the guidance of Dr. Rajesh Ramachandran, focusing on understanding the retina regeneration following injury in zebrafish. This project developed my interest in regeneration biology, which led me to join the lab of Dr. Grégoire Michaux, where I am currently investigating the atrophy and regeneration of microvilli in intestinal epithelial cells.
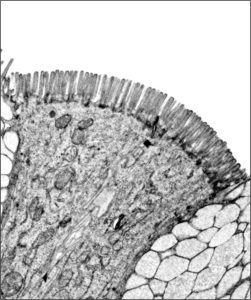
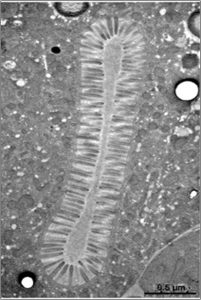
Electron micrograph showing Microvilli on the top side of intestinal cells in humans and C. elegans.
The top side of intestinal cells is decorated with numerous highly organized, finger-like projections called microvilli. These specialized structures form the brush border, which increases the absorptive surface area of the cell manyfold and is indispensable for nutrient uptake and organismal survival. Brush border atrophy can be caused by genetic diseases, pathogens, toxins, and often results in complications such as chronic diarrhea, which can prove fatal. Currently, our understanding of brush border atrophy is limited, and only preventive measures are available to mitigate the symptoms. Through this project, we are making an attempt towards understanding this process and developing regenerative approach in the hope of providing better alternatives to the treatments currently employed.
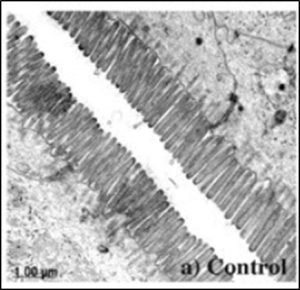
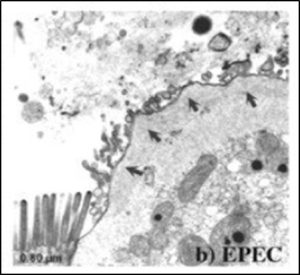
Electron micrograph showing damaged microvilli following bacterial infection in mouse intestine (Savkovic, S.D., et al. (2005).
We are using C. elegans as our model organism, which provides us with a robust genetic toolkit and features a simple intestine consisting of only 20 cells, each covered with microvilli. Moreover, we are using super resolution microscopy to understand the mechanisms behind the process, which could then be translated into human cell models and serve as a bedrock for the development of various treatments for microvilli-related intestinal diseases.
